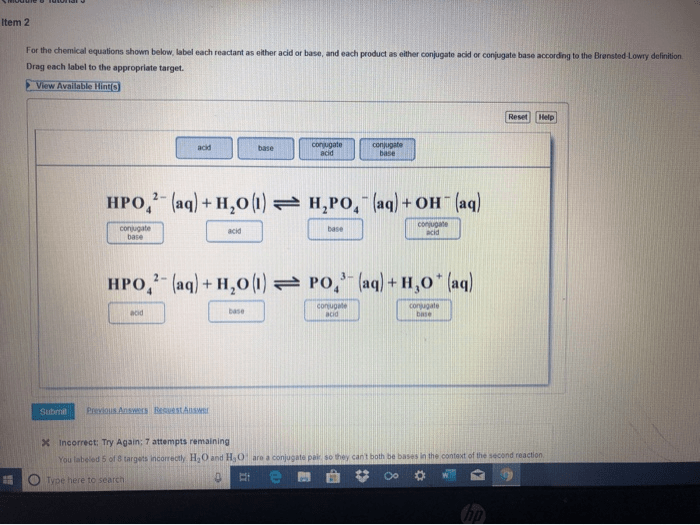
Label each reactant and product in the given chemical reaction. – Labeling reactants and products in a chemical reaction is a fundamental step in understanding the intricate dance of chemical transformations. This guide delves into the depths of this process, providing a comprehensive framework for identifying and labeling the key players in a chemical equation.
By defining reactants and products, establishing methods for their identification, and exploring the conventions for labeling them, this guide empowers students and practitioners alike to navigate the complexities of chemical reactions with clarity and precision.
Reactants and Products in Chemical Reactions: Label Each Reactant And Product In The Given Chemical Reaction.
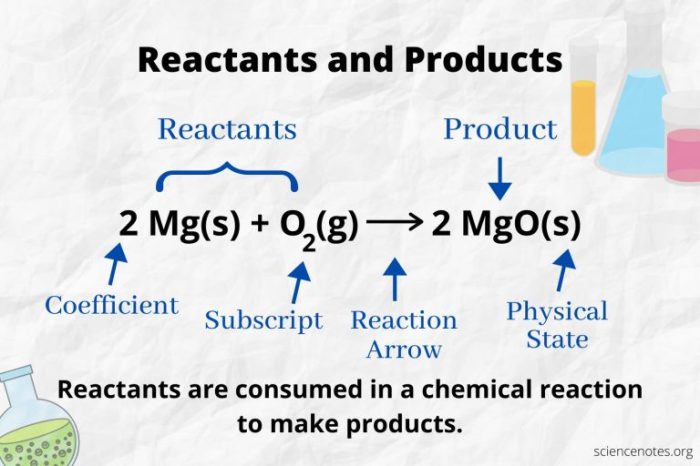
Chemical reactions involve the interaction of substances called reactants to form new substances called products. Understanding the concept of reactants and products is crucial in chemistry.
Defining Reactants and Products
Reactantsare the initial substances that participate in a chemical reaction and undergo a chemical change. They are written on the left-hand side of a chemical equation.
Productsare the new substances formed as a result of the chemical reaction. They are written on the right-hand side of a chemical equation.
Identifying Reactants and Products, Label each reactant and product in the given chemical reaction.
To identify reactants and products, consider the following:
- Reactants:Appear on the left side of the chemical equation and are typically separated by a plus sign (+).
- Products:Appear on the right side of the chemical equation and are typically separated by a yield arrow (→).
Labeling Reactants and Products
Labeling reactants and products in a chemical reaction helps identify their specific roles:
- Reactant 1:Labeled as R1
- Reactant 2:Labeled as R2
- Product 1:Labeled as P1
- Product 2:Labeled as P2
Table of Reactants and Products
| Reactant 1 | Reactant 2 | Product 1 | Product 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H2) | Oxygen (O2) | Water (H2O) | – |
| Sodium (Na) | Chlorine (Cl2) | Sodium Chloride (NaCl) | – |
| Methane (CH4) | Oxygen (O2) | Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | Water (H2O) |
Essential Questionnaire
What is the difference between a reactant and a product?
Reactants are the initial substances that undergo a chemical transformation, while products are the newly formed substances that result from the reaction.
How do I identify reactants and products in a chemical equation?
Reactants are typically written on the left-hand side of the equation, while products are written on the right-hand side.
Why is it important to label reactants and products?
Labeling reactants and products helps to clarify the roles of each substance in the reaction and facilitates the understanding of the overall chemical process.